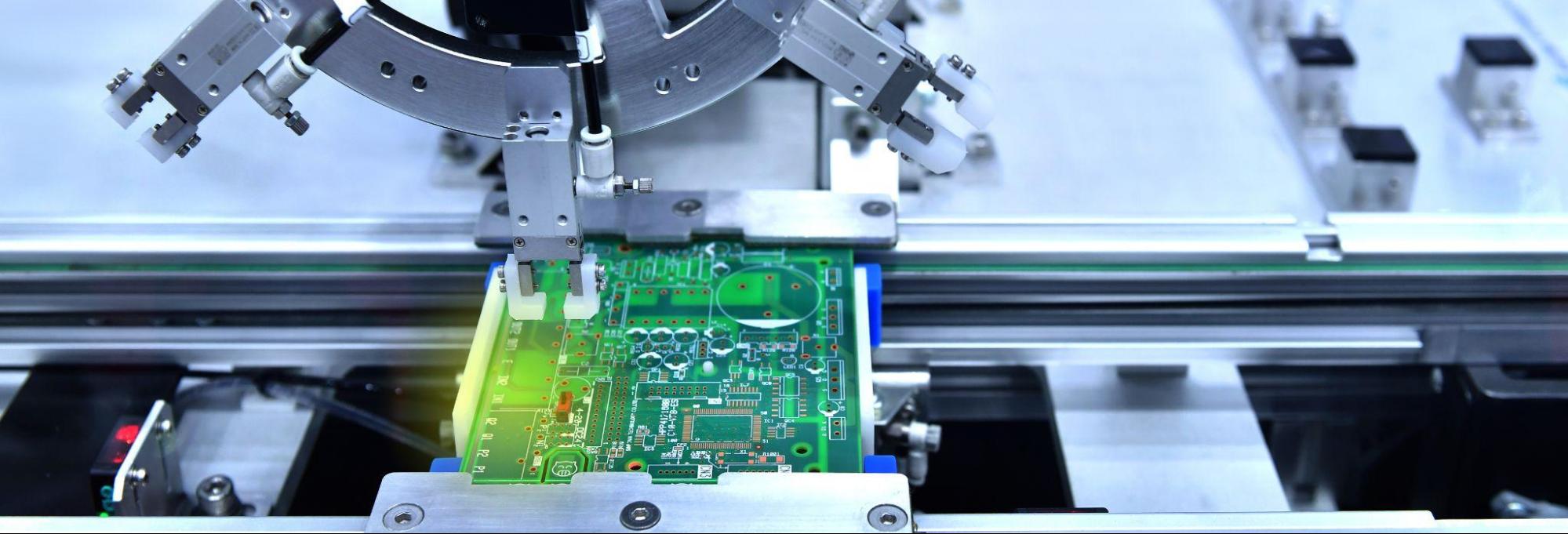
Rigid PCBs are the most commonly used circuit boards in the world. From the name itself, it is clear that they are made of materials that are not flexible. Therefore, after the manufacturing process, one cannot alter their shape or fold them. The most common material used for rigid boards is fiber-glass-based FR4 material.
The most reliable PCB assembly in Silicon Valley
Avoid component procurement delays by using a single vendor to source your parts. Transparent pricing. Fast turn-times. Learn more about our assembly services here.
Characteristics of rigid PCBs
Below are the characteristics of rigid boards:
- They are stiff and cannot be twisted or folded.
- The stiffness is due to the FR4 reinforcement.
- Copper traces and paths run across these boards which connect different components and layers..
- Modification of shape is not possible after fabrication.
- These PCBs can have single, double, or multilayer structures.
Rigid PCB assembly overview
Initially, the circuit board design and documentation take place followed by the actual rigid board assembly process.
Design and documentation
Below are a few important files and documents that are required before the assembly process begins.
- BOM file: The bill of materials lists all the electrical and mechanical parts used in the assembly.
- Neutral database file: A neutral CAD database is equally important to the assembly process as it is to the fabrication process.
- X-Y placement file: To program the automated placement machinery.
- Solder paste stencil artwork file: This file comes in the Gerber format and includes the details of how the solder should be screened through the stencils.
- Test point location files: Testing of the assembled boards ensure the accuracy of the process. This file includes all the test point locations to conduct the required tests of the circuit board.
- Schematic: The schematic is the basis of the PCB layout and can be in any format as per the choice of the board manufacturer.
- Assembly drawing: Indicates how the rigid PCB assembly should be performed.
Design for Assembly Handbook
6 Chapters - 50 Pages - 70 Minute ReadWhat's Inside:
- Recommended layout for components
- Common PCB assembly defects
- Factors that impact the cost of the PCB assembly, including:
- Component packages
- Board assembly volumes
Download Now
Assembly process
The rigid board assembly process can be simply put in the following stages:
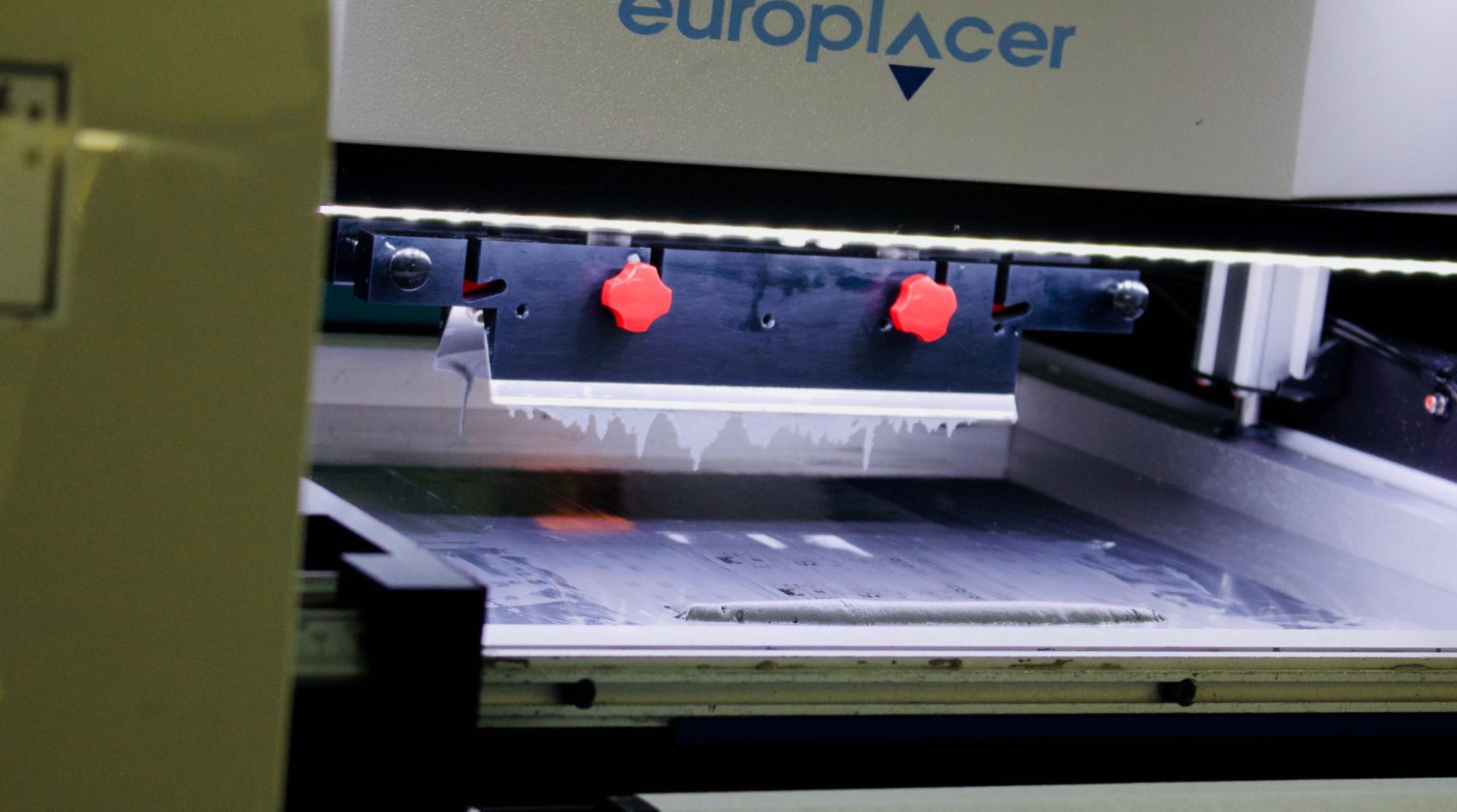
- Applying solder paste: Solder paste is applied using a stencil.
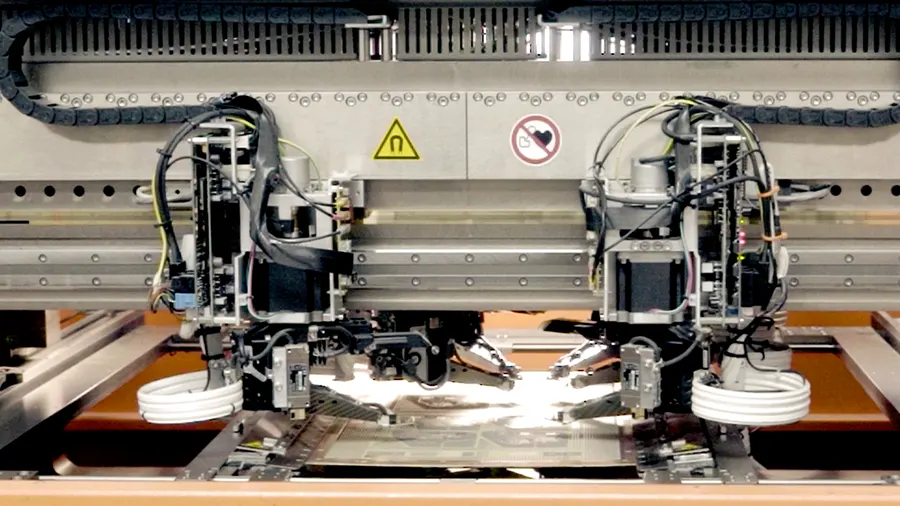
- Automated placement of SMT components: The panel moves along the placement line and the pick-and-place machine places the surface-mount components.
- Reflow soldering: Panels move to the reflow oven for soldering. Only surface-mount components are soldered using this process.
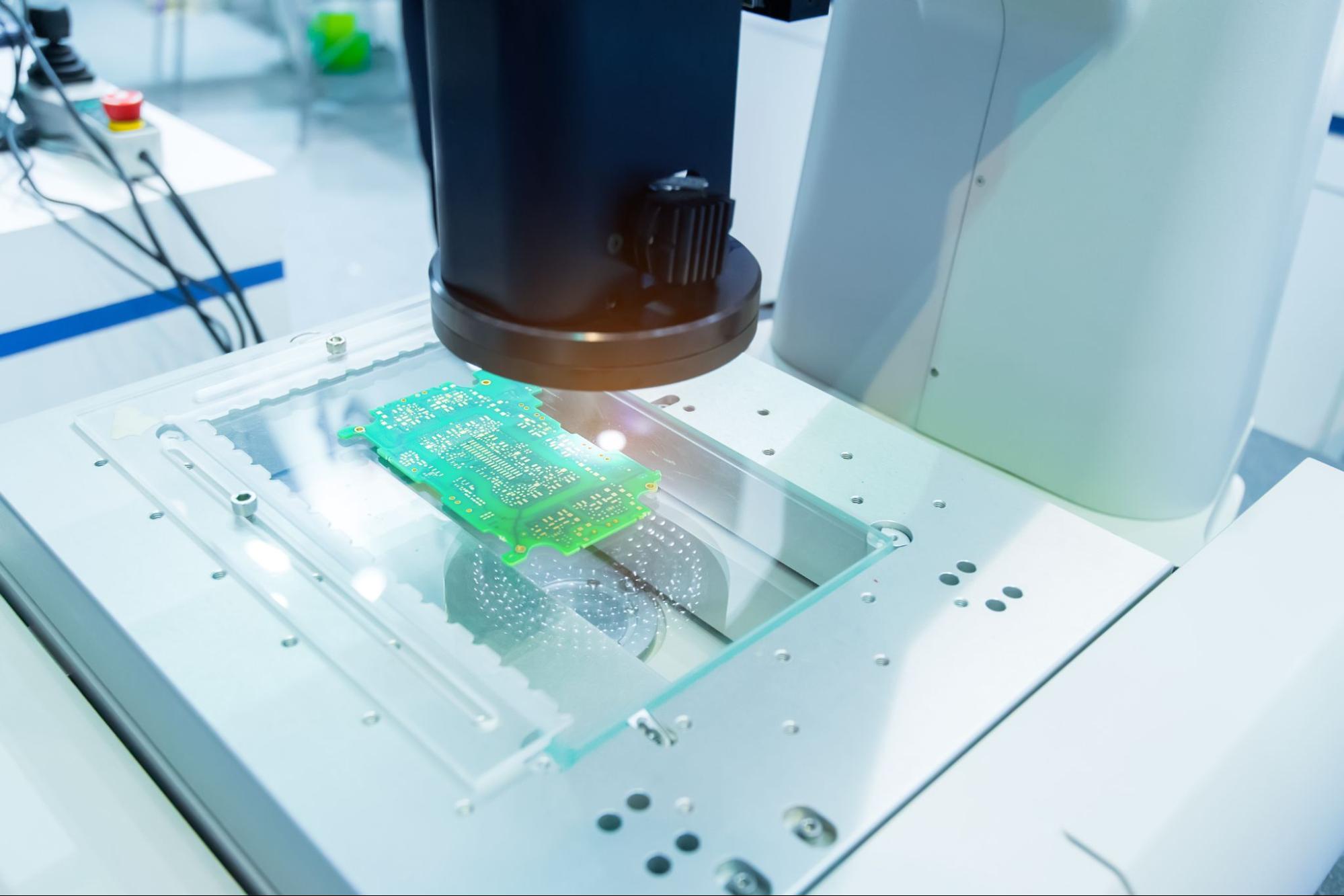
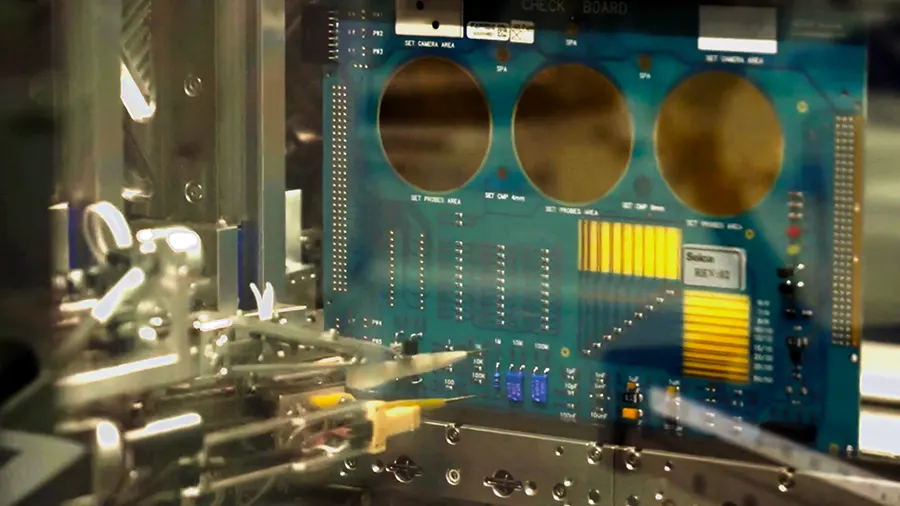
- Inspection: Automated optical inspection (AOI) or X-ray inspection is carried out to ensure proper soldering and placement of components.
- Through-hole component mounting: Through-hole components are placed on the rigid board.
- Wave/manual/selective soldering: For through-hole components, any one of the three soldering methods is used as per convenience.
- Cleaning: Once soldering is done, rigid PCBs are washed using deionized water/IPA to remove contaminants.
- Soldering of non-washable components: Components that are non-washable are only soldered to the board after the cleaning process is complete.
- Final inspection: Thorough inspection of the assembled components is done.
- Testing: Functional, in-circuit, or flying probe tests are done to ensure the quality of the assembly.
- Conformal coating: It protects the board from environmental conditions and moisture. It is not mandatory and depends on your requirements.
- Package and delivery: Once the board assembly is checked and verified for its functionality, it is properly packaged and sent for delivery.
This is how rigid PCBs are assembled. Proper planning and design can save a lot of time and bring down the cost of rigid board assembly.
One-stop PCB assembly services, capabilities, and testing
We source components from chip manufacturers across the globe, including Mouser, Digi-Key, Arrow Electronics and others. We also warehouse a significant inventory of common parts. If we cannot source a specific component, our engineers will make recommendations for fair-price alternatives.