What are the PCB materials used to fabricate a board?

A printed circuit board is manufactured using the following PCB materials:
Prepreg
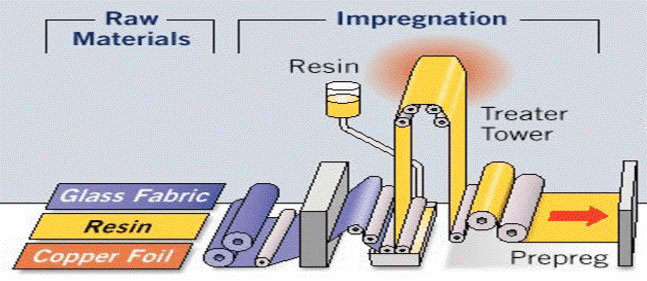
Prepreg is a glass fiber weave/cloth impregnated with a resin bonding agent. The glass fibers are interwoven to form a glass fabric. This fiber weave is partially dried to form a B-stage material. The resin is pre-dried, but not hardened. When it is heated, it flows and sticks. Prepregs are thus fiberglass strengthened by an adhesive layer.
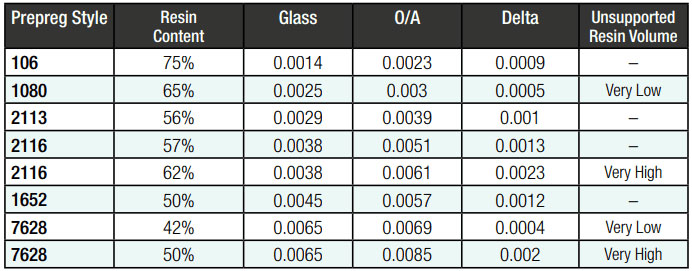
Depending on the resin content prepregs are classified as standard resin, medium resin, and high resin. The best PCB material is chosen depending on the desired final thickness, layer structure, or impedance.
Copper clad laminate
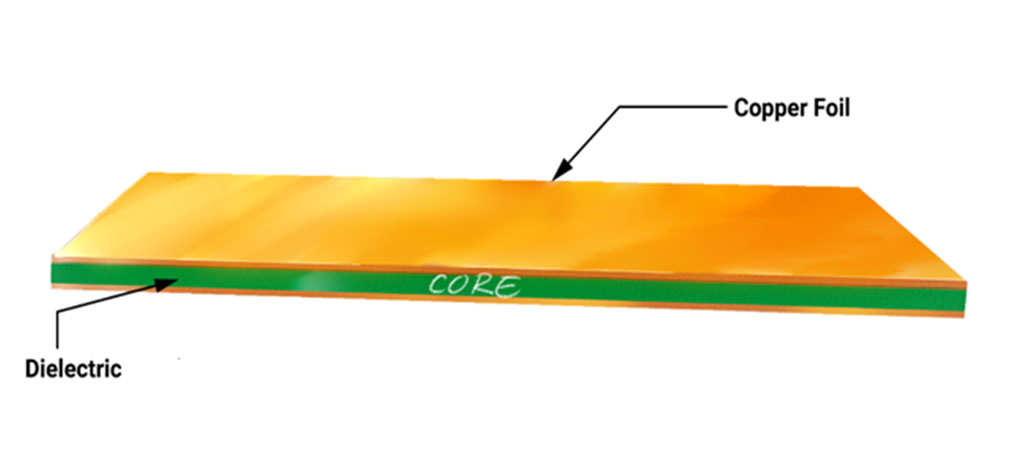
Plies of prepreg bonded together constitute the core of a circuit board. This core is cladded with the copper foil on either side to form a copper clad laminate (CCL).
Copper foil
Copper foil serves as a conductive layer on a board. Signals flow through the copper tracks etched on them. To learn more about copper features, see copper for PCBs.
How to choose dielectric materials?
Board substrates are made of dielectric materials. While choosing board laminates, you need to consider some of the crucial properties of the dielectric material implemented. These properties include:
Electrical properties Thermal properties Chemical properties Mechanical properties
Dielectric constant (Dk) Glass transition temperature (Tg) Moisture absorption Tensile modulus
Loss tangent and dissipation factor (Tan δ or Df)
Decomposition temperature (Td) CAF resistance Tensile strength
Dielectric electrical strength
Thermal conductivity (k)
Flexural strength
Coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)
For more details on electrical, thermal, chemical, and mechanical properties see PCB substrates.

PCB Material Design Guide
9 Chapters - 30 Pages - 40 Minute ReadWhat's Inside:
- Basic properties of the dielectric material to be considered
- Signal loss in PCB substrates
- Copper foil selection
- Key considerations for choosing PCB materials
Download Now
PCB material categories
Circuit board materials can be classified into four categories based on the signal loss properties.
1. Normal speed and loss: Normal-speed materials are the most common board materials – FR-4 family. Their dielectric constant (Dk) versus frequency response is not very flat and they have a higher dielectric loss. Therefore, their suitability is limited to a few GHz digital/analog applications. An example of this material is Isola 370HR.
2. Medium speed, medium loss: Medium-speed materials have a flatter Dk versus frequency response curve, and have a dielectric loss of about half that of normal speed materials. These are suitable for up to ~10GHz. An example of this material is Nelco N7000-2 HT.
3. High speed, low loss: These materials also have flatter Dk versus frequency response curves and low dielectric loss. They also generate less unwanted electrical noise compared to others. They are suitable for ~60GHz applications. An example of this material is Isola I-Speed.
4. Very high speed, very low loss (RF/microwave): Materials for RF/microwave applications have the flattest Dk versus frequency response and the least dielectric loss. They are suitable for up to ~100GHz applications and beyond. An example of this PCB material is Isola Tachyon 100G.
Circuit board material options
Normal/medium speed (0 - 10GHz)
| Manufacturer | Material name | Application areas |
|---|---|---|
| Isola | FR370HR | Medium speed, normal loss |
| Medium speed, normal loss | N7000-2 HT | Medium speed, medium loss |
High speed (10 - 30GHz)
| Manufacturer | Material name | Application areas |
|---|---|---|
| Isola | FR408HR | High speed, low loss |
| Isola | I-Speed | High speed, low loss |
| Panasonic | Megtron6 R-5775 | High speed, low loss |
| Isola | FR408HR | High speed, low loss |
Very high speed/microwave (20 - 60GHz)
| Manufacturer | Material name | Application areas |
|---|---|---|
| Isola | I-Tera MT40 | Very high speed/frequency, very low loss |
| Rogers | RO3003 | Very high speed/frequency, very low loss |
| Rogers | RO4350 B | Very high speed/frequency, very low loss |
| Isola | Tachyon-100G | Very high speed/frequency, very low loss |
| Isola | Astra MT77 | Very high speed/frequency, very low loss |
| Isola | I-Tera MT40 | Very high speed/frequency, very low loss |
Proper PCB material selection is important since it will affect the ability of the signal traces to carry current. Our Material Selector tool lets you choose the board material that suits your design requirements.