Related Categories — Controlled Impedance » PCB Design » Signal Integrity
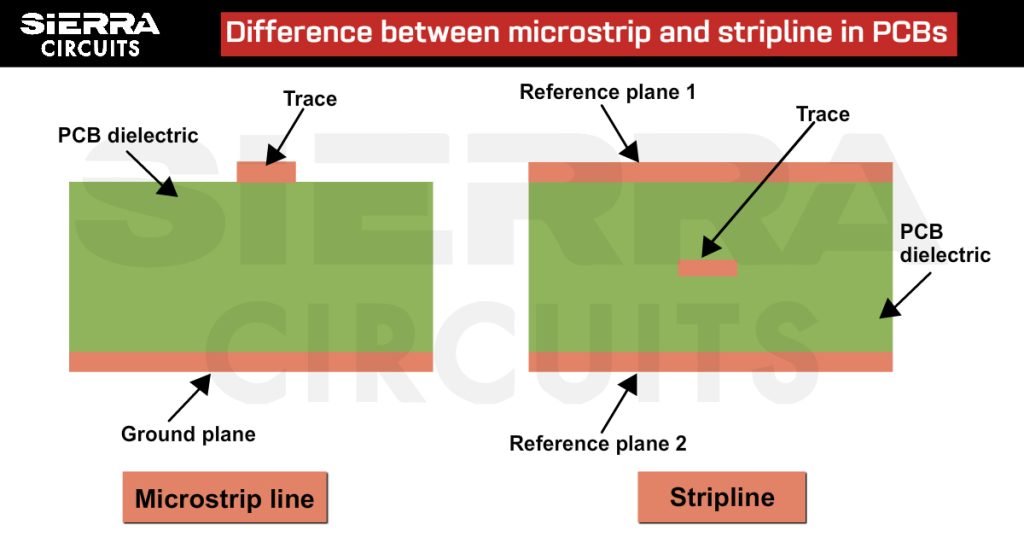
What Is the Difference Between Microstrip and Stripline in PCBs?
PCBs typically use two types of transmission lines: microstrips and striplines. Each of the transmission lines consists of a signal trace and a reference plane(s). Based on the transmission line geometry, it is essential to assume the signal trace and the reference plane as one unit.
Controlled Impedance
Controlled Impedance Routing Using Altium Designer
Controlled impedance is the characteristic impedance of a transmission line formed by PCB traces and its associated reference ... more »
Controlled Impedance
How to Control your Controlled Impedance
While manufacturing a PCB, controlled impedance can be achieved through specific dielectric thickness and by providing the target ... more »
Controlled Impedance
What Is the Difference Between Microstrip and Stripline in PCBs?
PCBs typically use two types of transmission lines: microstrips and striplines. Each of the transmission lines consists of ... more »
Controlled Impedance
Controlled Impedance Routing Using Altium Designer
Controlled impedance is the characteristic impedance of a transmission line formed by PCB traces and its associated reference ... more »
Controlled Impedance
How to Control your Controlled Impedance
While manufacturing a PCB, controlled impedance can be achieved through specific dielectric thickness and by providing the target ... more »
Controlled Impedance
9 Factors that Lead to Signal Integrity Issues in a PCB
Avoiding signal integrity issues in a PCB is an extremely complex task for designers. It requires a deep ... more »
Controlled Impedance
Measuring PCB, Cable and Interconnect Impedance, Dielectric Constant, Velocity Factor, and Lengths
Controlled impedance PCBs often include a measurement “coupon”, which typically includes sample traces, 6 inches long and constructed ... more »
Controlled Impedance
Fabrication, Procurement, & Assembly. PCBs fully assembled in as fast as 5 days.
- Bundled together in an entirely-online process
- Reviewed and tested by Engineers
- DFA & DFM Checks on every order
- Shipped from Silicon Valley in as fast as 5 days
Fabrication. Procurement & Assembly optional. Flexible and transparent for advanced creators.
- Rigid PCBs, built to IPC-6012 Class 2 Specs
- 2 mil (0.002″) trace / space
- DFM Checks on every order
- 24-hour turn-times available
Complex technology, with a dedicated CAM Engineer. Stack-up assistance included.
- Complex PCB requirements
- Mil-Spec & Class 3 with HDI Features
- Blind & Buried Vias
- Flex & Rigid-Flex boards